Fabio Gastaldello

Artistic image of the XMM satellite |
My main area of scientific expertise is the investigation of the physical properties of clusters and groups of galaxies which represent the current endpoint of cosmic structure formation and they are both cosmological tools and astrophysical laboratories. The main baryonic com- ponent of these systems, the hot gas constituting the intra-cluster and intra-group medium, is investigated through X-ray and SZ observations. Clusters and groups of galaxies are also among the best sources to be investigated through a multiwavelength approach, which allows for a thorough assessment of assumptions and systematics. During my scientific career I gained considerable experience in X-ray data analysis which is my main area of expertise. I obtained, analyzed and published results obtained with data from the major X-ray satellites in orbit in the last 20 years: XMM, Chandra, Suzaku, and NuSTAR, paying particular care at systematics caused by calibration issues and by the background treatment, crucial for the analysis of low surface brightness, extended sources |
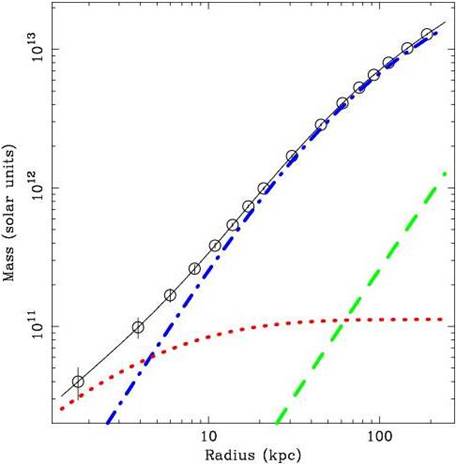
Mass profile of the NGC 1550 group. Black dots represents the total mass, blue line is the dark matter, green is the X-ray emitting gas, red the stars of the central galaxy |
Mass profiles of clusters and groups of galaxiesThe distribution of total and baryonic mass in galaxy clusters is a fundamental ingredient to validate the scenario of structure formation in a Cold Dark Matter (CDM) Universe. N-body simulations of structure formation within this paradigm indicate that DM halos show a NFW mass density profile characterized by a concentration and a virial mass with these two quantities related because the concentra- tion depends upon the assembly redshift. The concentration-mass relation, and its evolution in redshift, is therefore a strong prediction of CDM and is quite sensitive to the assumed cosmological parameters. In a series of papers (Gastaldello+07, Buote, Gastaldello et al. 2007, Ettori, Gastaldello et al. 2010) we demonstrated that the distribution of c-M values (with the additional constrains of the gas fraction) represent a mature and competitive technique in the era of precision cosmology. The key assumption in the above mentioned studies using high quality X-ray observations to perform mass reconstruction is hydrostatic equilibrium (HE). Recently with the XCOP data (X-ray + SZ) we have derived HE mass profiles out to the virial radius with unprecedented accuracy, quantifying a low level of non-thermal pressure support and hydrostatic bias (Ettori+19, Eckert+19). Joint studies with galaxy dynamics and lensing are mandatory to assess the validity of HE, the systematics affecting our mass measurements and to calibrate the most promising X-ray observable-mass relations like YX or the total gas mass, Mgas. In the X-ray follow-up of strong lensing systems at the galaxy group scale we discovered the lowest mass system currently known showing baryon-Dark matter separation, the Bullet Group (Gastaldello+14). |
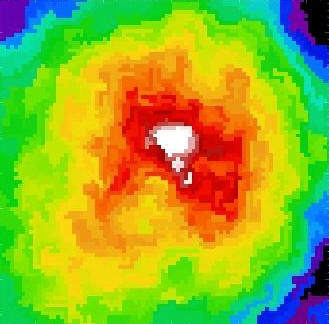
X-ray cavities and filaments in the Chandra image of the NGC 5044 group |
Physics of the ICM and IGM (intra-group medium)The micro-physics of the plasma of the ICM is relatively unknown and through the investigation of phenomena such as AGN feedback related features (cavities) and cold fronts we can further advance our under- standing. The topic of AGN feedback has been investigated in detail at the scale of massive clusters, less intensively at the scale of groups and poor clusters. We have been actively ex- ploring AGN feedback in the brightest nearby galaxy groups (e.g. AWM 4, Gastaldello+08, and NGC 5044, Gastaldello+09) and we have discovered the first sloshing cold front at the group mass scale (Gastaldello+09). |
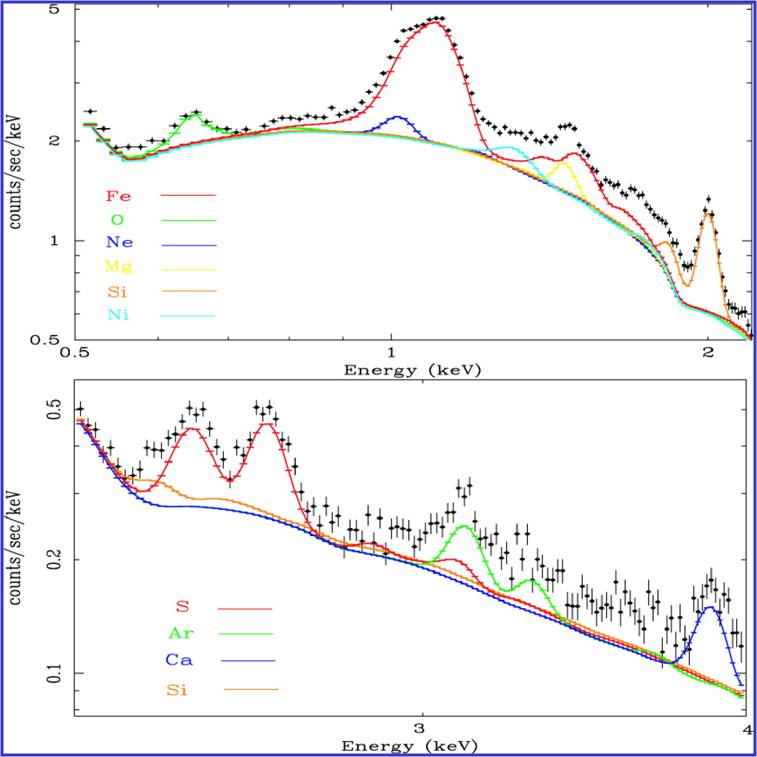
Spectral lines of metals in the spectrum of M87 |
Chemical enrichment of the ICM and IGMIf we need a model for the formation and evolution of galaxy clusters and groups which deal with both the cold (stars) and hot (ICM and IGM) phases together we should start from the metals which are the most direct link between the two. Many of the interpretative tools, in particular for the determination of the relative contribution of SNIa and SNII were developed in my work on the metal abundances in M87 (Gastaldello & Molendi 2002). I have been particularly active in the investigation of possible s ystematic errors in the measurement of the metal abundances, deriving from a fitting a single thermal model to a spectrum showing components at different temperatures (Fe bias in M87, Molendi & Gastaldello 2001, and inverse Fe bias in A2028, Gastaldello+10) and from the possible presence of resonant scattering (Gastaldello & Molendi 2004). The most interesting studies address the redshift evolution of cluster abundance which is an extremely challenging measurement with current instruments (see Baldi+12, Ettori+11). |
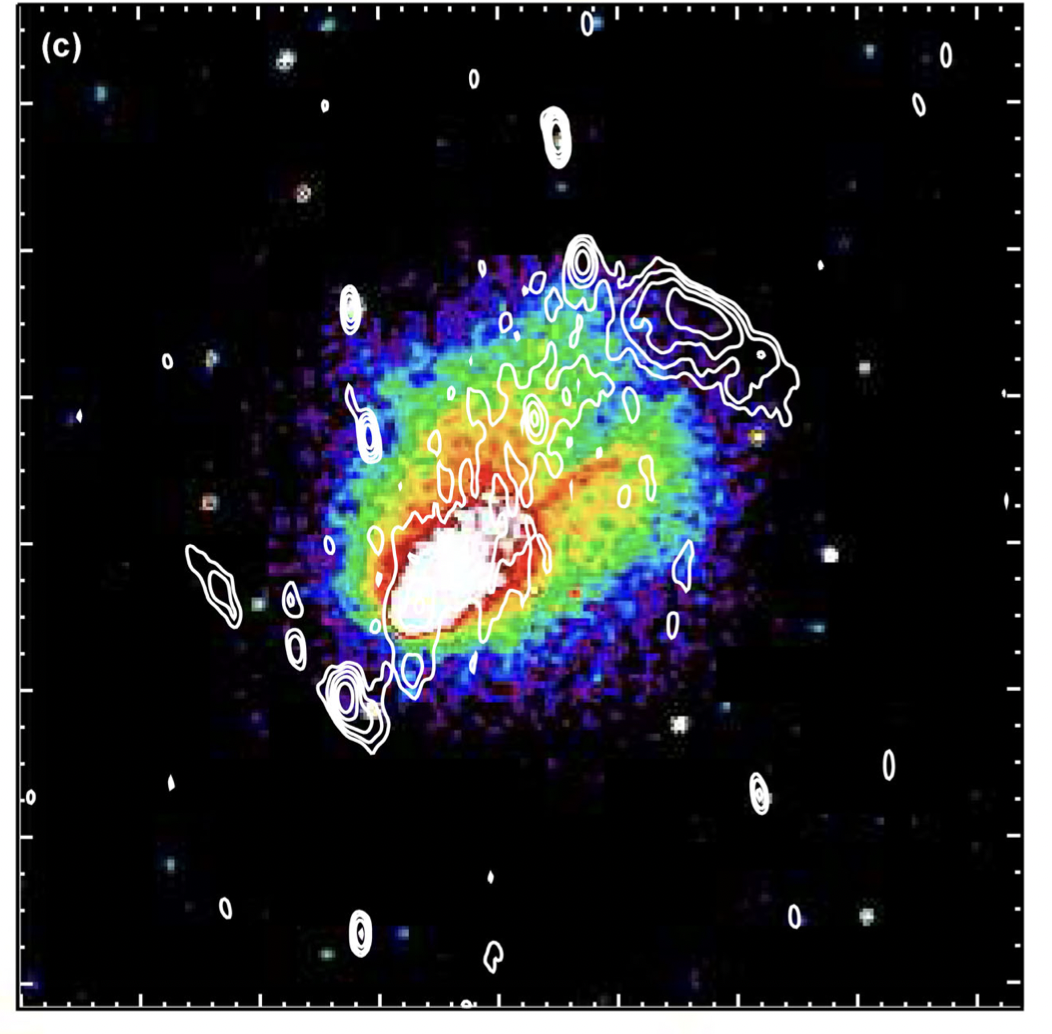
X-ray image of the El Gordo cluster with overlyed the radio contrours of its NW relic |
Non-thermal emission and particle acceleration in clusters of galaxiesThe characterization of non-thermal component provides much needed clues on the physical process presiding over the formation and evolution of clusters. In some of the more disturbed objects, evidence of non-thermal processes has been known for quite some time. Radio observations indicate that merging clusters are often the site of cluster-wide synchrotron emission, the so called radio halos and radio relics. The detection of inverse Compton (hereafter IC) emission at X-ray wavelengths can provide an alternative method to estimate cluster magnetic fields. Detection and characterization of this emission is highly uncertain and con- troversial. The launch of NuSTAR, the first focusing telescope in the range 10-80 keV is providing progress in the field, establishing solid upper limits on the IC component (Wik+14, Gastaldello+15). We also started a program to look for shock features and constraints on particle acceleration processes in a sample of radio relic clusters (Botteon, Gastaldello et al. 2016a, 2016b, 2018). |
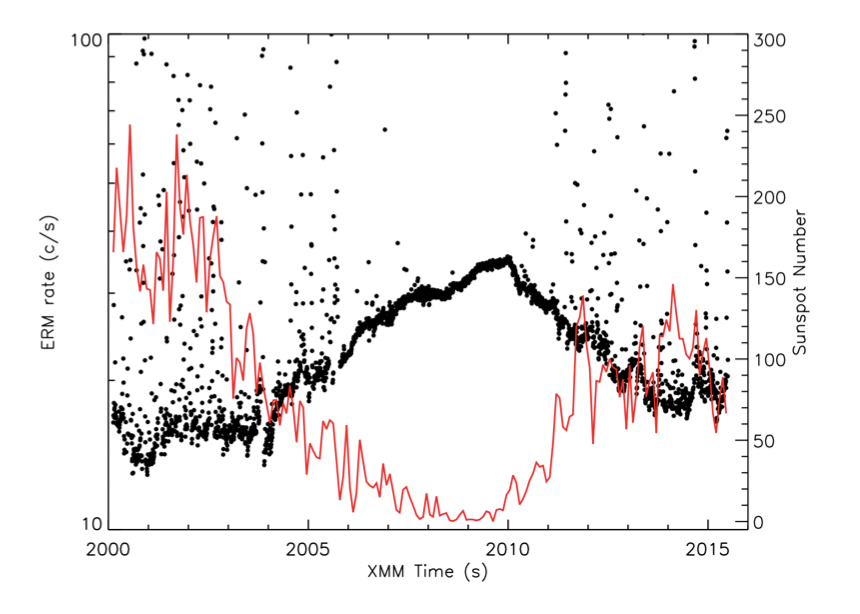
The median count-rate of the EPIC Radiation Monitor for each XMM orbit. The number of sun-spot is overplotted with a red line |
Background characterization, calibration of current satellites and future missions designas already highlighted the science to be performed on galaxy clusters requires a good knowledge of the response of the instrument (calibration) and a careful treatment of the background and of its systematic. I have been particularly active in the calibration and background characterization of XMM and NuSTAR and involved in cross-calibration activities with other satellites, Chandra and Suzaku, through the International Astronomical Consortium for High Energy Calibration (IACHEC) and my own work. I have been active in the mission design of NHXM and now of Athena, in particular in designing strategies for its background minimization (Gastaldello+18). |